Prostatitis - inflammation and swelling of the tissues of the prostate gland (prostate).And with such a disappointing diagnosis, 50% of men aged 18-50 years are faced.
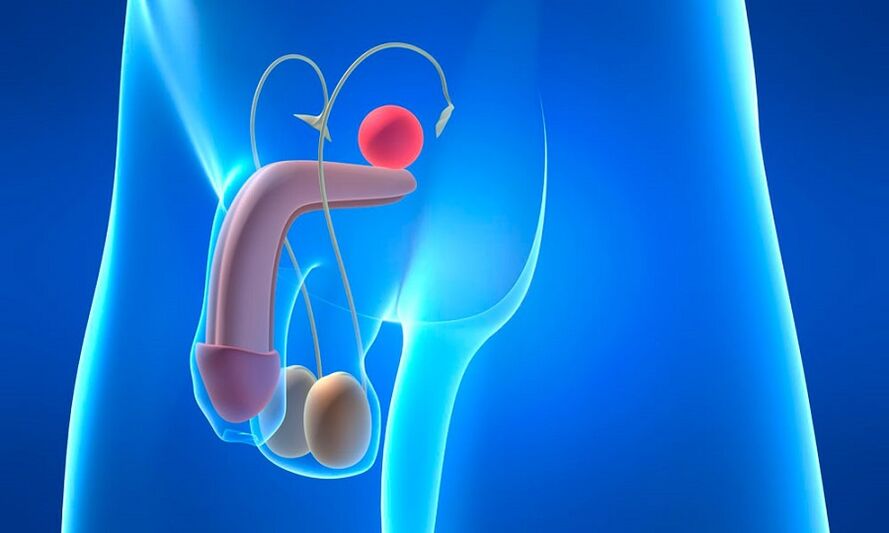
The disease usually develops slowly, without obvious signs and for many years brings a minimum of concern to its owner.
A man has been living with prostatitis for years, does not consult a doctor and allows the disease to go into a chronic form with serious complications.
When the patient nevertheless reaches the clinic, it happens too late: prostatitis goes into malignant education or leads to infertility.So what are the first signs of the disease and how to deal with it?
Symptoms
Prostate disease in men has characteristic symptoms and requires immediate treatment.But the disease is insidious.Sometimes its signs have not been manifested for years.
Meanwhile, the inflammatory process is slowly developing, striking more and more new tissues and leading to impotence and infertility.
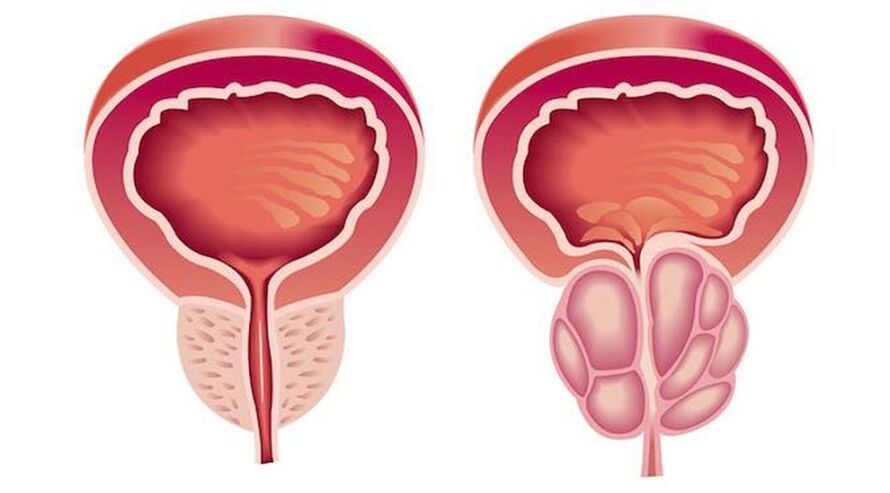
In order not to launch the disease, a man must pay attention to the characteristic features that accompany any type of prostatitis:
- pain and burning in the perineum, lower abdomen, in the region of the scrotum and in the zone where the prostate is located;
- rapid urination, weak stream, the appearance of pus from the urethra in the form of white fibers or flakes;
- fast or, conversely, prolonged ejaculation (sometimes painful), long night erection, sexual dysfunction, decrease in sexual desire;
- deterioration in sperm quality, change in its quantity;
- fatigue and irritability, general weakness.
Signs of the disease can all appear together or declare themselves separately;Sometimes they are so implicit that they are written off for fatigue or lack of sleep.If a man notices at least one of the above symptoms, he needs to visit a doctor.
It should not be considered that problems with the prostate gland are the destiny of people who have crossed the threshold of the 30th anniversary.Prostatitis can occur in any sexually mature man, and now people are increasingly getting sick of 18–20 years.
The causes of the disease
Prostatitis in men is provoked by various reasons:
- long abstinence from sexual life, stagnation and poor blood circulation in the organs of the genitourinary system;
- injuries, hypothermia, age -related changes;
- sexual infections, viruses, bacteria.
In combination with factors that create a favorable situation for damage to the body, these reasons are caused by inflammation of the prostate gland.
Risk factors:
- erratic or irregular sex life, artificial lengthening or interruption of sexual intercourse;
- sedentary, sedentary lifestyle;
- transferred infections, chronic diseases of the organs of the genitourinary system;
- Excess weight;
- reduction of immunity, tendency to allergies, hormonal malfunctions;
- frequent hypothermia;
- untimely emptying of the bladder and irregular defecation;
- stress and emotional overload;
- excessive physical activity or lifting heavy objects;
- smoking and alcoholism;
- Lack of vitamins, micro- and macro elements.

If a man’s body experiences at least one of the above factors, he has a high probability of prostatitis.In this case, it is advisable to undergo a preventive inspection every six months.
Types
Prostatitis can occur in different forms and generate different reasons.Depending on this, it is divided into different types.
A large number of varieties of prostatitis leads to the fact that in each case, individual treatment should be prescribed.Do not listen to the advice of friends and their reviews about drugs.What helped in one case will be completely ineffective in another.
Acute prostatitis
It develops due to the effects of pathogenic microorganisms on the tissue of prostate, which penetrate the prostate gland from the urethra or bladder and lead to inflammation.
Sometimes acute prostatitis occurs after chronic infectious diseases - sinusitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, caries - or due to hormonal disorders.
Signs of acute prostatitis manifest themselves intensively:
- constant weakness, fatigue, malaise;
- a slight increase in temperature;
- pain in the groin, anus, sometimes spreading to the back, lower back and legs;
- rapid urination, the inability to completely empty the bladder, weak pressure, thread, urinary retention;
- lack of erection, violation of ejaculation;
- Purulent discharge from the urinary channel.
Acute prostatitis is dangerous in that inflammation spreads rapidly, affecting the nearby organs.Sometimes this leads to an extensive abscess of a nearby tissue and to blood vessel thrombosis.

Typically, treatment is carried out not at home, but in a hospital.If therapy was competent, acute prostatitis is completely cured.
If the treatment turned out to be untimely or insufficient, the disease goes into a chronic form.
Chronic prostatitis
It becomes a consequence of unbearable acute infectious prostatitis (bacterial form) or occurs due to injury, hypothermia (abacterial form).
Symptoms of chronic prostatitis during the period of remission are almost never manifested.
A man can note:
- discomfort or weak pulling pain in the groin;
- rapid urination, weakening of the jet;
- constant weakness, apathy;
- decrease in sex drive.
How is chronic prostatitis manifested during the exacerbation?
It is accompanied by symptoms characteristic of an acute state.Chronic prostatitis is distinguished by a wave -like course: after exacerbation, a period of remission certainly occurs.
Men prefer to wait out the acute period and forget about the disease for several months.Few people go to the doctor.
Infectious prostatitis
The cause of infectious prostatitis is damage to the tissues of the prostate gland with viruses, bacteria or fungi.
According to the type of microorganism, the following varieties of infectious prostatitis are distinguished:
- bacterial (Escherichia or prayed wand, staphylococcus, streptococcus);
- viral (herpes virus, human papillomas, cytomegalovirus);
- mycoplasmic (mycoplasma);
- Trichomonade (Trichomonade);
- gonorrhea (gonococcus);
- chlamydia (chlamydia);
- tuberculosis (Koch stick);
- fungal (Candida fungus);
- mixed.
Symptoms of infectious prostatitis repeat signs of acute form of the disease.
If the disease is not treated, it leads to the occurrence of a purulent process, which quickly extends to all nearby organs.This condition that threatens the patient’s life becomes an indication for surgical intervention.
Calcular prostatitis
Its cause is stones in the prostate gland.This form is found in men, old age, who have abandoned the treatment of a chronic disease.
The symptoms of calculous prostatitis are similar to the symptoms of a chronic disease, but sometimes they are supplemented by specific signs:
- pain in the sacrum and bottom of the back, which intensifies after walking, prolonged sitting or sexual contact;
- the presence of blood in sperm.
Most often found when an ultrasound pass.
Stagnant prostatitis
It arises due to the stagnation of the prostate or blood in the veins that penetrate this organ.Stagnant phenomena are a consequence of irregular sexual life, wearing close underwear, hypodynamia or alcohol abuse.
Symptoms with this form of the disease are weak, resemble signs of chronic prostatitis.
Complications
Each type of prostatitis has its consequences for the body.
For example, acute prostatitis, unbearable in time, goes into a chronic form or leads to the following complications:
- purulent inflammation of the prostate gland;
- edema of the prostate;
- acute urine delay.
Typically, such consequences appear infrequently, since acute prostatitis brightly declares himself, and the man goes to the doctor.
Much more troubles can cause chronic prostatitis, which manifests itself not so obvious and develops for a longer time.
Complications of chronic prostatitis and its consequences for male health:
- Prostate fabric sclerosis;
- cystitis, pyelonephritis;
- impotence;
- prostate abscess;
- vesiculite, epididymitt;
- infertility;
- Calcular formations in the bladder and prostate gland;
- renal failure;
- Adenoma and prostate cancer.
With neglected chronic prostatitis, many pathological changes are irreversible.For example, urination problems and sexual dysfunction will no longer be eliminated by simply curing prostatitis.
Diagnostics
If characteristic symptoms occur, a man needs to visit a urologist or andrologist.The doctor makes the diagnosis of acute prostatitis on the basis of a survey, examination of the patient, a finger of rectal examination and analysis of the secret of the prostate.
Typically, these studies do not cause discomfort, but during exacerbation they can cause pain.
The study of the secret of the prostate allows you to identify the nature of the disease - bacterial or abacterial.With a bacterial origin of prostatitis, a secret is also studied on resistance to antibacterial drugs.
Chronic inflammation is more difficult to detect.
For this, a whole complex of laboratory and hardware techniques is used:
- bacteriological sowing of the secret of prostate and urine to determine the infection;
- biochemical analysis of venous blood to determine the level of ESR, dog and leukocytes;
- analysis of urethral discharge;
- Urofluometry;
- prostate biopsy;
- Ultrasound (through the abdominal wall) and Trusi (through the rectum);
- MRI and CT of the damaged organ;
- Urodynamic study;
- urethrocystoscopy;
- X -ray examination.
Why can not be diagnosed only on the basis of clinical manifestations of prostatitis?
The fact is that the doctor should identify not only the presence of the disease, but also its cause in order to choose effective treatment.
If acute prostatitis can be eliminated in 1 course of therapy, then the chronic is treated much longer.Sometimes the patient becomes a regular visitor to the urologist’s office.The more correctly the treatment will be selected and the more precisely the patient will follow the doctor’s recommendations, the more the period of remission will be.
How to treat prostatitis?
Treatment of prostatitis is a long process that occupies at least 1.5 months and involves a whole range of procedures.
The key to successful therapy is a timely appeal to the clinic, the high professionalism of the doctor, the correct diagnosis and clear compliance by the patient with all the recommendations of the specialist.
With prostatitis, comprehensive treatment is prescribed, which includes taking anti -inflammatory drugs and antibiotics at the stage of exacerbation and physiotherapy and massage at the remission stage.Separately, these methods will not bring the desired effect.
Drug therapy
Therapy with drugs lasts 3-4 weeks and includes taking the following groups of drugs:
- non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs for eliminating pain and inflammation;
- antibacterial drugs (fluoroquinols, cephalosporins, penicillins, macrolides, tetracycline) for the treatment of bacterial prostatitis and disease caused by hypothermia;
- immunomodulators, vitamin and mineral complexes to stimulate the body's defenses;
- hormonal drugs to eliminate hormonal imbalance and stagnation of the prostate gland in its tissues;
- Musorelaxants and alpha-blockers for relaxing muscles (eliminate inflammation of the prostate gland, relieve the spasm of urethra and bladder, facilitate the process of urination).

Particularly effective drugs that are produced in the form of rectal suppositories.
They are faster than tablets and injections, deliver the active substance in the tissue of the prostate and have the best healing effect.
Acute prostatitis is treated with medication until the disease enters the stage of remission.In advanced cases, the patient is sent to a hospital and assigned up to 5 groups of antibiotic drugs at the same time.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Physiotherapy is used as an auxiliary treatment and is used only in combination with medications.
It is impossible to treat the prostate with physiotherapeutic devices until the symptoms of exacerbation are completely eliminated.
Types of physiotherapy:
- electrical stimulation;
- laser treatment;
- Diadinamophoresis;
- transrectal magnetotherapy;
- phonophoresis and phototherapy;
- reflexology;
- hirudotherapy;
- Prostate massage.
Physiotherapy gives the best results for chronic and stagnant prostatitis.
But with an infectious and calculusal disease, you should refuse massage - it will only help the infection to spread faster to nearby organs or will drive stones.
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment can be radical (removal of the prostate) or sparing (removal of part of the prostate or injection to reduce it).
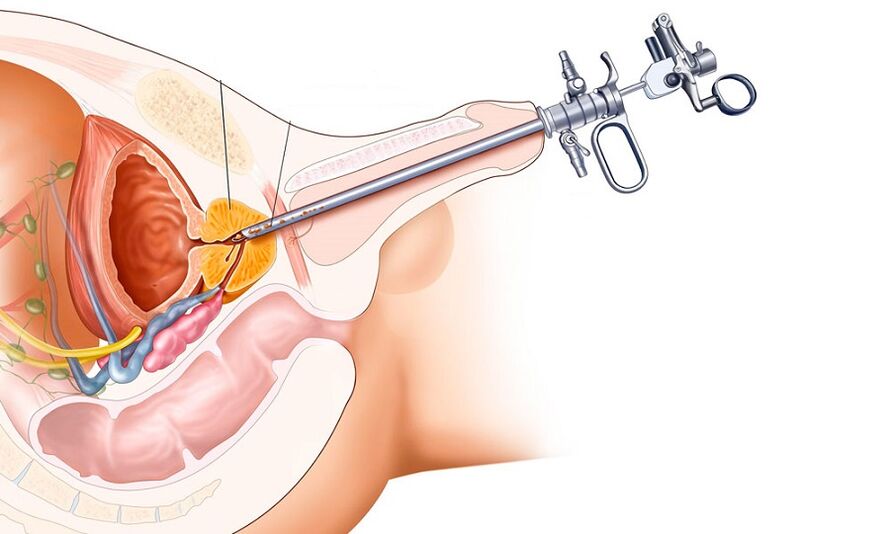
Indications for the operation:
- narrowing of the urethra, phimosis of the penis and acute urinary retention;
- purulent process in prostate tissues and in nearby organs;
- stagnation of the secret of the prostate in its cavity due to the improper functioning of the seed bubbles;
- stones in the prostate cavity;
- Prostate adenoma or sclerotic changes in its tissues.
What is prostate adenoma in men?This is a benign education, which is most often treated with surgical methods.It is a consequence of chronic prostatitis and occurs in men after 50 years.
This type of treatment is not the best option, since it is aimed at the result of the disease, and not for its cause.
In addition, he is not able to return the lost health: he will only slow down the development of the disease.
Folk remedies
Famous folk recipes should be applied only as an addition to the main treatment prescribed by a doctor.
Folk medicines:
- reception of chamomile decoctions, calendula, birch buds, sage;
- drinking alcohol tinctures of St. John's wort and echinacea;
- wearing urological plasters with extracts of medicinal herbs;
- The use of candles with propolis, ichthyol or sea buckthorn candles.

It is impractical to use folk drugs as the main treatment.
They will not be able to slow down the course of the disease or cure it, and the precious time will be lost.
Prevention
Preventive measures are aimed at eliminating factors contributing to the development of prostatitis, and a timely diagnosis of an existing disease.
Prevention measures:
- strengthening immunity;
- rejection of random sexual relations;
- timely treatment of infectious and sexually transmitted diseases;
- rejection of smoking and excessive alcohol consumption;
- healthy diet, exclusion from the diet of spicy and smoked foods, carbonated drinks, energy;
- stress with stress;
- avoiding hypothermia and overheating;
- wearing free underwear from natural materials;
- Regular sports, exercise therapy (jogging, sports walking, press exercises, squats, “birch”), long walks.
To prevent prostatitis, the right sex life is important.Phenomena such as artificially protracted or interrupted sexual intercourse, repeated sexual intercourse are completely unacceptable.

Sexual life should be regular: it is unacceptable for prolonged abstinence, as well as sexual arousal, not ending with ejaculation.
Also, each man should undergo a preventive inspection with a urologist every six months.The doctor will notice the signs of a beginning disease and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Prostatitis in the initial stages is much easier to cure than a disease that has become chronic.